Otoacoustic Emissions
An otoacoustic emissions (OAE) device is a vital tool for ENTs, audiologists and other hearing health professionals. These instruments range from fully clinical and diagnostic to screening and handheld or portable options. There are also combination devices that have more than one modality. A clinical OAE device will be the most versatile device and include with a number of test types such as DPOAE, TEOAE, Spontaneous OAE, I/O function, and microfine points per octave to assist with diagnosis and verification of outer hair cell function. Screening OAEs include predefined protocols that provide a pass or refer result with either DPOAE, TEOAE, or both.
GSI OAE Devices
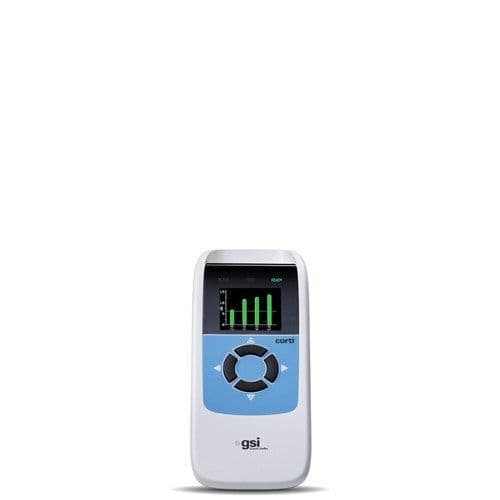
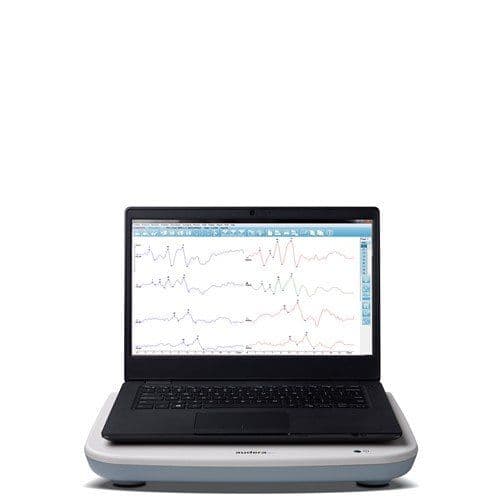
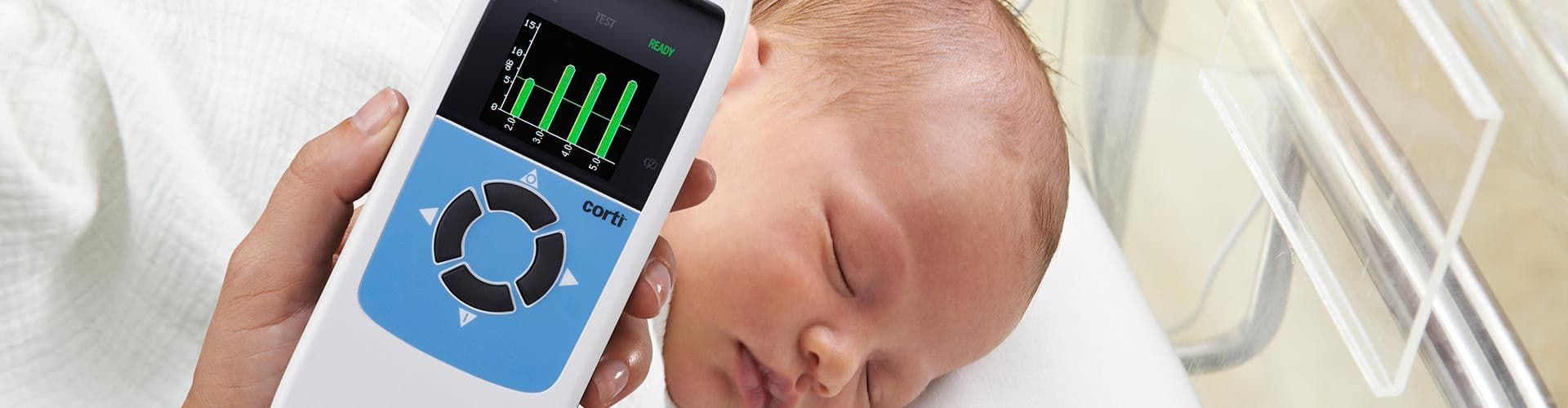
There are multiple options for testing OAEs available with GSI. The GSI Corti™ is a portable diagnostic and screening device that can be customized to measure DPOAE and/or TEOAE. The GSI Audera Pro™ is a clinical evoked potentials instrument that can be configured with OAE testing capabilities. The GSI Novus is a newborn hearing screener that can be used for AABR and OAE. Select a product below to learn more!

OAE FAQ
Find more educational materials about OAEs by visiting the GSI Education Page.
What is an Otoacoustic Emissions Test?
An OAE test assesses the function of outer hair cells in the cochlea. It requires no active participation from the patient. An OAE machine analyzes the outer hair cell function by sending a sound into the ear. When a sound is sent into a normal functioning ear system, the outer hair cells will generate sounds (otoacoustic emissions) that can be measured by a sensitive microphone placed in the ear canal. If returning sounds are not detected by the device, the patient needs to have additional hearing testing to verify hearing status.
How are OAE Tests Performed?
An OAE hearing test machine is used to measure outer hair cell function. To conduct an OAE hearing test, a small probe that generates a calibrated stimulus is placed into the ear canal. The stimulus is sent into the ear canal and the OAE response is measured through a very sensitive microphone in the same probe. The device screen displays the result as either “pass” or “refer.” Refer indicates that additional testing is needed to verify hearing status.
What is the Difference Between Screening and Diagnostic OAE Testing?
Screening OAE testing is a basic evaluation that provides an automated result and is typically performed by technicians or medical assistants. No interpretation is required as the equipment uses sophisticated algorithms to assign a pass or refer result. Screening OAE testing is used in universal newborn hearing screening programs and for pre-school and school hearing screenings. Diagnostic OAE testing is a more comprehensive evaluation of outer hair cells that is used in conjunction with other tests designed to diagnose hearing loss, like audiometry and tympanometry. Diagnostic OAE tests are performed by licensed hearing healthcare professionals such as audiologists and require knowledge of the auditory system to interpret the test results.
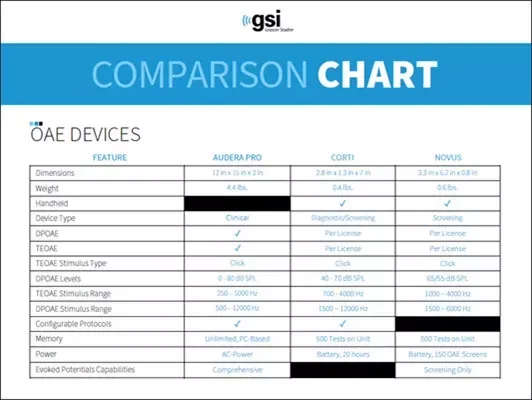
OAE Device Comparison Chart
| Feature | Audera Pro | Corti | Novus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensions | 12 in x 15 in x 3 in |
2.8 in x 1.3 in x 7 in |
3.3 in x 6.2 in x 0.8 in |
| Weight | 4.4 lbs. |
0.4 lbs. |
0.6 lbs. |
| Handheld |
|
✔ |
✔ |
| Device Type | Clinical |
Diagnostic/Screening |
Screening |
| DPOAE |
✔ |
Per License |
Per License |
| TEOAE |
✔ |
Per License |
Per License |
| TEOAE Stimulus Type | Click | Click | Click |
| DPOAE Levels | 0 - 80 dB SPL |
40 - 70 dB SPL | 65/55 dB SPL |
| TEOAE Stimulus Range | 250 – 5000 Hz |
700 - 4000 Hz | 1000 – 4000 Hz |
| DPOAE Stimulus Range | 500 –12000 Hz |
1500 –12000 Hz | 1500 –6000 Hz |
| Configurable Protocols |
✔ |
✔ |
|
| Memory |
Unlimited, PC-Based |
500 Tests on Unit |
500 Tests on Unit |
| Power | AC-Power |
Battery, 20 hours | Battery, 150 OAE Screens |
| Evoked Potentials Capabilities |
✔ |
Screening Only | |
| GSI Suite Compatible |
|
✔ |
|
| Other Data Management | Audera Pro Database |
Corti Data Manager, HearSIM | HearSIM |
| IDEAL ENVIRONMENT | AUDERA PRO | CORTI | NOVUS |
| Private Practice |
✔ |
✔ |
|
| ENT |
✔ |
✔ |
|
| Hospital |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
| University |
✔ |
✔ |
|
| Newborn Screening Program |
✔ |
✔ |
|
| Schools |
✔ |
||
| Veterans Affairs |
✔ |
✔ |