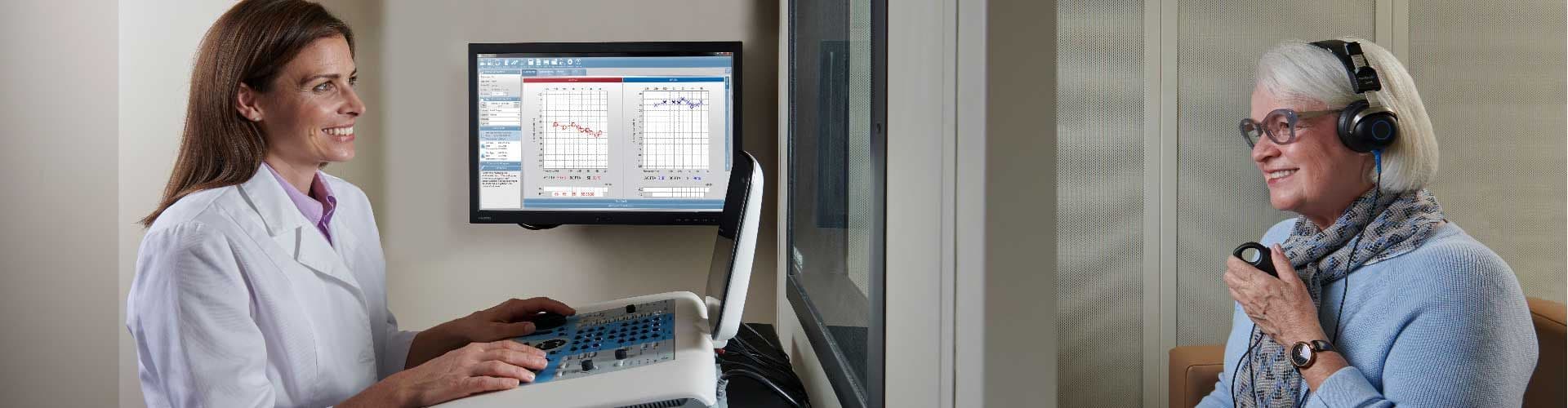
Audiometers
An audiometer is used to measure a patient’s ability to hear at different levels. Different audiometer types include clinical 2 channel audiometers, mid-level 1.5 channel diagnostic audiometers, and 1 channel air conduction screening audiometers. A clinical audiometer is the most versatile device that allows the clinician complete flexibility when performing basic and advanced audiometric evaluations on patients of all ages. Both air and bone conduction, along with speech audiometry, can be performed with a clinical audiometer. Integrated special tests such as speech in noise testing and word recognition tests are included so clinicians can test a broad range of patients.
A diagnostic audiometer is used to identify the type and severity of hearing loss. The device allows for basic diagnostic testing and sometimes includes the option to upgrade to specific special tests. A screening audiometer can identify the need for further audiometric testing. It is limited to pure tone screening audiometry.
The right type of audiometer enables audiologists to screen and diagnose a broad range of patients in their practices. Depending on what they need, they may want to choose an audiometer with the capability to do tone testing, speech testing, or more. GSI offers a wide range of reliable screening and diagnostic audiometers to meet your clinical and screening needs.
GSI Audiometers
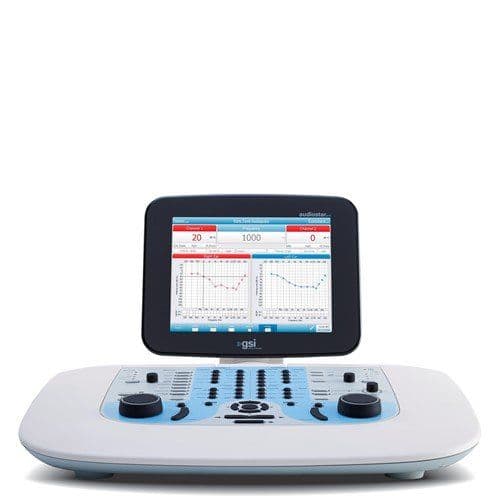
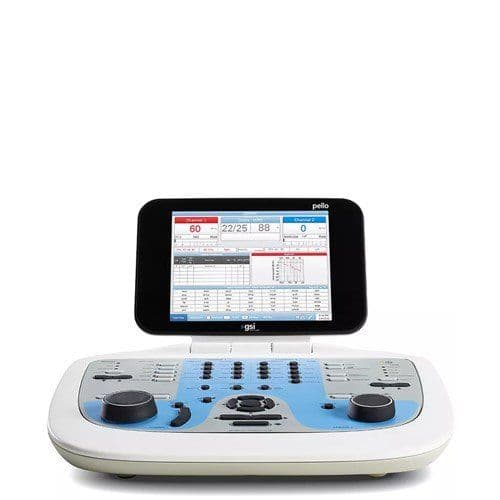
There are currently a number of audiometer options available with GSI. The GSI AudioStar Pro™ is a full two channel clinical audiometer designed to perform efficient audiometric evaluations on every patient population. The GSI Pello™ is an adaptable audiometer with several licensing options available based on the clinic’s needs. The GSI 18™ is a portable screening audiometer. The GSI 39™ is a combination screener that has both audiometry and tympanometry capabilities. Grason-Stadler also has two options available for automated audiometry testing: GSI AMTAS Pro™, a diagnostic automated audiometry software run on a touchscreen computer connected to an audiometer, and GSI AMTAS Flex™, a tablet automated audiometry solution. Select a product below to learn more!
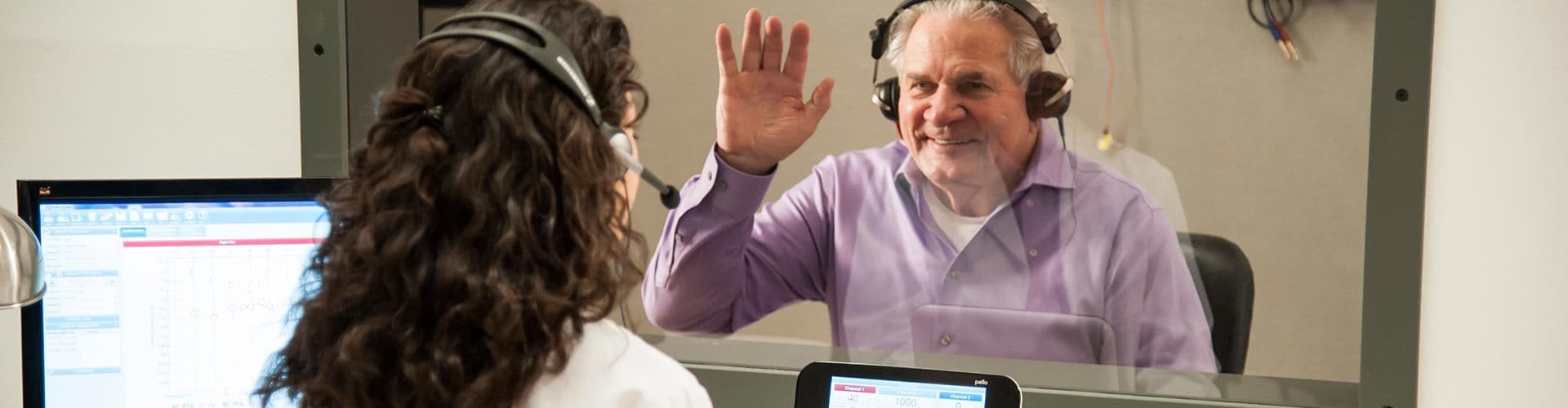

Audiometer FAQ
Find more educational materials about audiometry by visiting the GSI Education Page.
What is an Audiometer?
An audiometer is a medical device used by those who test a patient’s hearing, such as an audiologist or clinician. This is done by presenting sounds at various frequencies and levels to the patient.
What is an audiometer used for?
An audiometer is used to evaluate a patient’s hearing. While the tones and/or words are presented to the patient via the audiometer, the clinician records the patient’s thresholds. This allows them to assess the patient’s hearing abilities and diagnose any potential hearing loss. Using this information, an appropriate treatment plan can be developed.
What is the difference between diagnostic and screening audiometry?
Screening audiometry is used to simply identify if conductive hearing loss is an issue for the patient. The clinician will most commonly perform pure tone audiometry testing to present tones to the patient and find out at which decibel levels there may be hearing loss.
If the screening audiometry testing concludes that there is hearing loss, the next step would be to use diagnostic audiometry to try and identify what exactly is going on that is causing the hearing loss and how extensive the damage is. Using this information, the clinician can determine the best course of action for the patient.
What will an audiogram tell you?
An audiogram is a graph of the softest sounds a patient can hear at different frequencies or pitches. The results of a hearing test are plotted on the audiogram to describe a patient’s hearing. The audiogram can give information on the type and severity of a patient’s hearing loss. This information can help determine the most appropriate next step. This may include additional testing, medical referral, or hearing aids.
What types of environments are audiometers used in?
Audiometers are used in several testing environments. At audiology and ENT clinics, screening and diagnostic audiometry may be used to as a vital part of obtaining an entire hearing healthcare profile of a patient. In schools, the school nurse may use an audiometer for routine screening of children to identify if students may have a potential hearing issue. This is important to identify hearing loss as early as possible so a plan of action can be made before it affects the student’s communication skills and development.
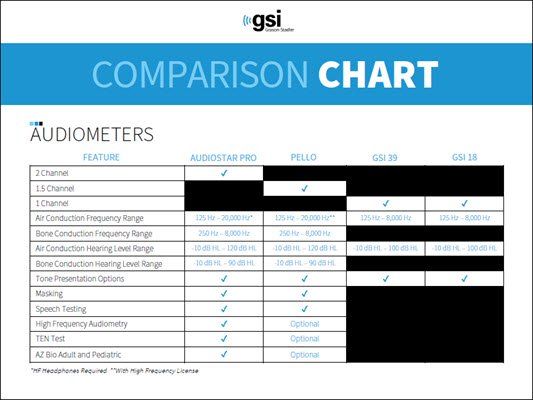
Audiometer Comparison Chart
| Feature | AudioStar Pro | Pello | GSI 39 | GSI 18 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 Channel |
✔ |
|||
| 1.5 Channel |
✔ |
|||
| 1 Channel |
✔ |
✔ |
||
| Air Conduction Frequency Range | 125 Hz – 20,000 Hz* | 125 Hz – 20,000 Hz* | 125 Hz – 8,000 Hz | 125 Hz – 8,000 Hz |
| Bone Conduction Frequency Range | 250 Hz – 8,000 Hz |
250 Hz – 8,000 Hz | ||
| Air Conduction Hearing Level Range | -10 dB HL –120 dB HL | -10 dB HL –120 dB HL | -10 dB HL –100 dB HL | -10 dB HL –100 dB HL |
| Bone Conduction Hearing Level Range | -10 dB HL - 90 dB HL | -10 dB HL - 90 dB HL | ||
| Tone Presentation Options |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
| Masking |
✔ |
✔ |
||
| Speech Testing |
✔ |
✔ |
||
| High Frequency Audiometry |
✔ |
Optional | ||
| TEN Test |
✔ |
Optional | ||
| AZ Bio Adult and Pediatric |
✔ |
Optional | ||
| QuickSIN |
✔ |
Optional | ||
| BKB-SIN |
✔ |
Optional | ||
| Pure Tone Stenger |
✔ |
✔ |
||
| Speech Stenger |
✔ |
✔ |
||
| Insert Headphones |
✔ |
✔ |
Optional | Optional |
| Super-aural Headphones |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
| Sound Field Speakers | Optional | Optional | ||
| GSI AMTAS | Optional | Optional | ||
| ACT Test |
✔ |
Optional | ||
| Portable |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
|
| Patient Response Button |
✔ |
✔ |
Optional | Optional |
| Custom Configurations |
✔ |
✔ |
||
| GSI Suite Reporting |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
|
| 100+ Word Lists |
✔ |
✔ |
||
| Tympanometry |
✔ |
|||
| Width x Depth x Height | 20.1 in x 14.6 in x 13.2 in | 14.8 in x 10.5 in x 13.8 in | 12.5 in x 14.5 in x 4.7 in | 12.6 in x 8.8 in x 3.2 in |
| Weight | 17 lbs. | 8.2 lbs. | 5 lbs. | 2.5 lbs. |
*HF Headphones Required **With High Frequency License