Speech Audiometry
AUDIOMETRY GUIDES
Introduction
Speech audiometry is an important component of a comprehensive hearing evaluation. There are several kinds of speech audiometry, but the most common uses are to 1) verify the pure tone thresholds 2) determine speech understanding and 3) determine most comfortable and uncomfortable listening levels. The results are used with the other tests to develop a diagnosis and treatment plan.
SDT = Speech Detection Threshold, SAT = Speech Awareness Threshold. These terms are interchangeable and they describe the lowest level at which a patient can hear the presence of speech 50% of the time. They specifically refer to the speech being AUDIBLE, not INTELLIGIBLE.
This test is performed by presenting spondee (two-syllable) words such as baseball, ice cream, hotdog and the patient is to respond when they hear the speech. This is often used with non-verbal patients such as infants or other difficult to test populations. The thresholds should correspond to the PTA and is used to verify the pure tone threshold testing.
How to Test:
Instruct the patient that he or she will be hearing words that have two parts, such as “mushroom” or “baseball.” The patient should repeat the words and if not sure, he or she should not be afraid to guess.
Using either live voice or recorded speech, present the spondee word lists testing the better ear first. Start 20 dB above the 1000 Hz pure tone threshold level. Present one word on the list and, if the response is correct, lower the level by 5 dB. Continue until the patient has difficulty with the words. When this occurs, present more words for each 5 dB step.
Speech Reception Threshold (SRT)
SRT, or speech reception threshold, is a fast way to help verify that the pure tone thresholds are valid. Common compound words - or spondee words - are presented at varying degrees of loudness until it is too soft for the patient to hear. SRT scores are compared to the pure tone average as part of the cross check principle. When these two values agree, the reliability of testing is improved.
Word Recognition
Instruct the patient that he or she is to repeat the words presented. Using either live voice or recorded speech, present the standardized PB word list of your choice. Present the words at a level comfortable to the patient; at least 30 dB and generally 35 to 50 dB above the 1000 Hz pure tone threshold. Using the scorer buttons on the front panel, press the “Correct” button each time the right response is given and the “Incorrect” button each time a wrong response is given.
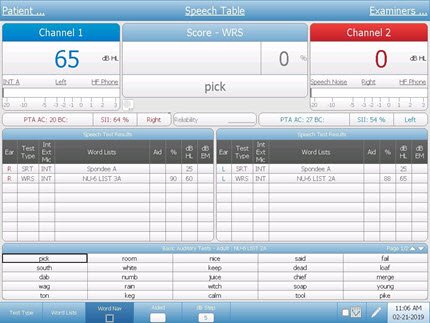
The Discrimination Score is the percentage of words repeated correctly: Discrimination % at HL = 100 x Number of Correct Responses/Number of Trials.
WRS = Word Recognition Score, SRS = Speech Reception Score, Speech Discrimination Score. These terms are interchangeable and describe the patient’s capability to correctly repeat a list of phonetically balanced (PB) words at a comfortable level. The score is a percentage of correct responses and indicates the patient’s ability to understand speech.
Word Recognition Score (WRS)
WRS, or word recognition score, is a type of speech audiometry that is designed to measure speech understanding. Sometimes it is called word discrimination. The words used are common and phonetically balanced and typically presented at a level that is comfortable for the patient. The results of WRS can be used to help set realistic expectations and formulate a treatment plan.
Speech In Noise Test
Speech in noise testing is a critical component to a comprehensive hearing evaluation. When you test a patient's ability to understand speech in a "real world setting" like background noise, the results influence the diagnosis, the recommendations, and the patient's understanding of their own hearing loss.
Auditory Processing
Sometimes, a patient's brain has trouble making sense of auditory information. This is called an auditory processing disorder. It's not always clear that this lack of understanding is a hearing issue, so it requires a very specialized battery of speech tests to identify what kind of processing disorder exists and develop recommendations to improve the listening and understanding for the patient.
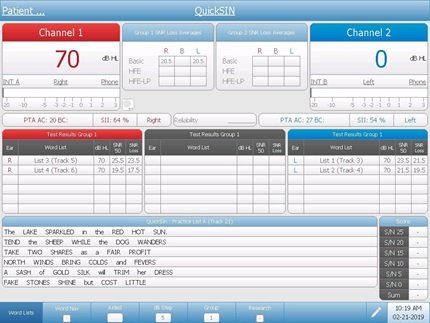
QuickSIN
QuickSIN is a quick sentence in noise test that quantifies how a patient hears in noise. The patient repeats sentences that are embedded in different levels of restaurant noise and the result is an SNR loss - or Signal To Noise ratio loss. Taking a few additional minutes to measure the SNR loss of every patient seen in your clinic provides valuable insights on the overall status of the patient' s auditory system and allows you to counsel more effectively about communication in real-world situations. Using the Quick SIN to make important decisions about hearing loss treatment and rehabilitation is a key differentiator for clinicians who strive to provide patient-centered care.
BKB-SIN
BKB-SIN is a sentence in noise test that quantifies how patients hear in noise. The patient repeats sentences that are embedded in different levels of restaurant noise an the result is an SNR loss - or signal to noise ratio loss. This test is designed to evaluate patients of many ages and has normative corrections for children and adults. Taking a few additional minutes to measure the SNR loss of every patient seen in your clinic is a key differentiator for clinicians who strive to provide patient-centered care.